스포츠 중계권 시장 분석
핵심 인사이트
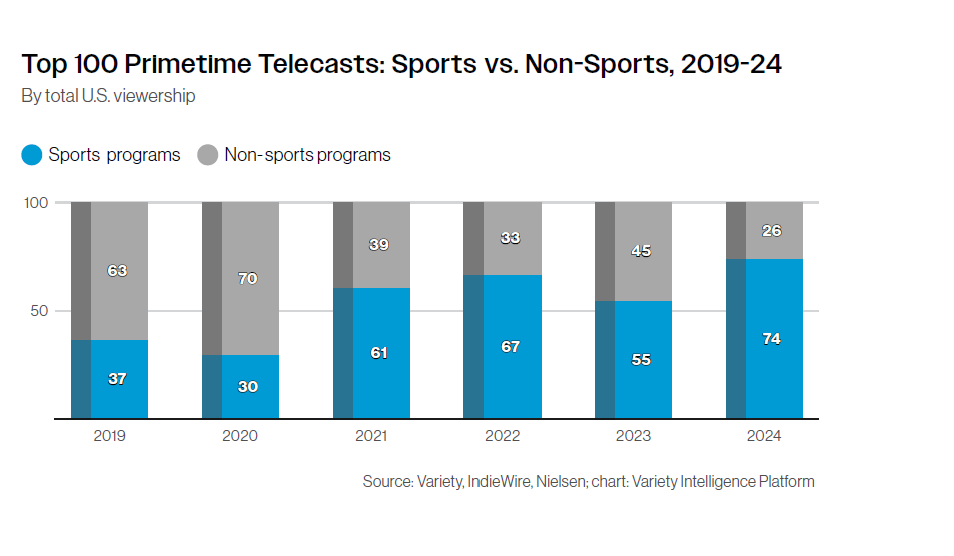
수십 년 동안 TV 네트워크를 설립하거나 강화하는 가장 확실한 방법은 라이브 스포츠 중계권을 확보하는 것이었다. 스포츠는 지속적으로 많은 시청자를 전통 TV로 끌어들이는 마지막 남은 장르다. 지난 6년 동안 닐슨의 프라임타임 시청률 상위 100위 안에 드는 스포츠 프로그램 수가 37개에서 74개로 두 배나 증가했다.
TV 시청자 수가 해마다 줄어들고 있음에도 불구하고, 스포츠는 여전히 방송사에 안정적인 시청자를 제공하며, 일부 소비자들이 아직 코드 커팅(케이블 TV 구독 해지)을 하지 않는 주요 이유이기도 하다. 하지만 이 장르가 너무 많은 시청자를 끌어들이다 보니, 전통 TV의 최대 경쟁자인 스트리밍 서비스들도 이 시장에 뛰어들고 있다.
The Volatile Sports Rights Market: The War Between TV and Streaming
Key Insights
For decades, the surest way to establish or strengthen a TV network has been securing live sports broadcasting rights. Sports remains the last genre that consistently draws large audiences to traditional TV. In just the past six years, the number of sports programs ranking in Nielsen's top 100 primetime broadcasts has doubled from 37 to 74.
Despite TV viewership declining year after year, sports continues to provide networks with reliable audiences and remains a key reason why some consumers haven't yet cut the cord. However, because this genre attracts so many viewers, streaming services—traditional TV's biggest competitors—are also jumping into this market.
스트리밍 서비스의 시장 진입
스트리머들은 라이브 TV 분야에 진출을 가속화하기 위해 최근 몇 년간 협상 테이블에 자리를 잡고, 장기간 중계권을 보유해온 기존 방송사들로부터 스포츠 중계권 계약을 가져가고 있다. 이들 회사는 그 권리에 대해 엄청난 금액을 제공할 의향이 있으며, 때로는 예상 수익을 명백히 초과하는 비용을 지불하기도 한다. 하지만 여기에는 좋은 이유가 있다: 스포츠는 중계권 계약의 수지 타산을 넘어서는 혜택을 제공할 수 있기 때문이다.















